SO2 EMISSION CONTROL
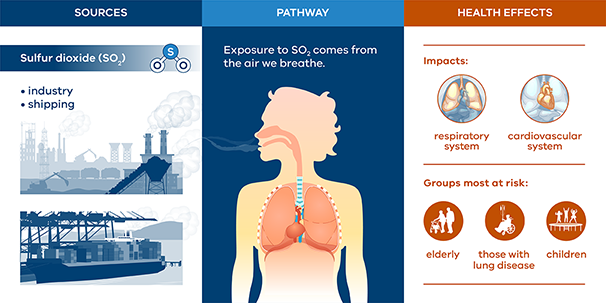
·
An examination by
the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA) has viewed as under 8%
of India's coal-based power plants have introduced the SO2 outflow decrease
innovation suggested by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC)
to keep Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) discharges in line.
·
A study conducted
in 2019 by Greenpeace asserts that India is the world's largest SO2 emitter.
What
are the Innovations to Diminish SO2 Emanations?
Flue
Gas Desulfurization (FGD):
·
The removal of
sulfide compounds from the exhaust emissions of fossil-fueled power plants is
known as FGD.
·
This is finished
through the expansion of sponges, which can eliminate up to 95% of the sulfur
dioxide from the vent gas.
·
When fossil fuels
like coal, oil, natural gas, or wood are burned for heat or power, flue gas is
produced.
Circulating
Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC)-
·
By simultaneously
injecting air and lime for burning, the CFBC Boiler is an environmentally friendly
power facility that reduces emissions of pollutants like nitrogen oxide and
sulfur oxide.
·
When a
pressurized fluid (liquid or gas) passes through a medium and causes the solid
particles to behave like fluids under certain conditions, the bed of solid particles
is said to be fluidized. Fluidization causes the change of the condition of
strong particles from static to dynamic.
What
were the study's most important findings?
·
Just a
consolidated limit of 16.5 Gigawatts(GW) of coal plants have introduced FGDs
and Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC) boilers identical to 5.9 GW
across India.
·
According to the
CREA analysis, 92% of the country's coal power plants operate without FGDs.
·
The derailment of
emission controls from coal-based electricity generation units was largely
caused by the blanket extension of the deadline for all coal power plants
without MoEF&CC and CPCB checking on their progress.
·
The MoEF&CC
presented outflow guidelines in 2015 for controlling PM, SO2, NOx, and Hg
(Mercury) emanations.
·
For units in
Delhi and the National Capital Region (NCR), the deadline has been extended
four times, while it has been extended three times for the majority of units
nationwide.
·
India currently
has 425 GW of installed energy generation capacity. Coal makes up 48.6 percent
of the total installed capacity, followed by gas at 5.9 percent, lignite at
1.6%, and diesel at less than 0.2 percent.
How
are power plants categorized for FGD installation?
·
In 2021, the
MoEF&CC separated the classes of coal-power plants in view of geology to
implement cutoff times.
·
Coal-based power
plants within a 10-kilometer radius of the National Capital Region (NCR) and
cities with more than a million people fall under Category A.
·
Class B is inside
a 10 km range of fundamentally dirtied regions or non-fulfillment urban
communities.
·
The remaining
plants across the nation are included in Category C.
·
With the longest
deadlines, the majority of the country's power plants are in Category C.
·
The independent
Center for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA) investigates trends, causes,
and health effects of air pollution as well as potential solutions.
·
It supports the
efforts of governments, businesses, and advocacy groups worldwide to move
toward clean energy and clean air by utilizing scientific data, research, and
evidence.
ONION EXPORT BAN
·
The Director
General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) has issued a notification reversing the
"Free" to "Prohibited" status of the onion export policy
until March 2024.
·
Onion prices have
significantly increased as a result of the current supply shortage brought on
by the anticipated lower kharif output in 2023 and the early depletion of
stocks for the rabi season in 2022-23.
·
The public
authority has likewise reexamined as far as possible for wheat, as far as
possible has been divided to 1,000 tons for wholesalers, and for retailers to 5
tons.
Why has the Public authority Prohibited
Product of Onion Cost?
Control of prices:
·
The government
wants to keep domestic market prices from rising or falling by limiting onion
exports.
·
To battle
spiraling costs, the Middle had forced a Base Commodity Cost of USD 800 for
every ton on onions in October 2023. In August, the government imposed an
export duty of forty percent on onions.
·
An export ban
helps to stabilize the price of onions, making them more affordable for local
consumers. Onions have a long history of experiencing significant price
volatility.
Getting
Rid of Scarcity:
·
A lack of onions
in the country can be caused by things like bad weather, less production, or
more demand.
·
The government
ensures that the available supply is used to meet domestic demands first by
prohibiting exports.
Food safety:
·
Onions are a
staple in Indian cooking, and any shortage can influence food security. The
government ensures that the population has access to this necessary food item
without experiencing shortages or unaffordable prices by reducing exports.
What are the Vital Realities About
Onion?
·
Onion is a
significant green wares become overall for their culinary purposes and
restorative qualities.
·
After China,
India is the second largest onion producer.
·
The major
onion-producing states are Maharashtra, Karnataka, Orissa, Uttar Pradesh,
Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
·
In 2021 and 2022,
Madhya Pradesh takes second place with a share of 15.16 percent, followed by
Maharashtra with a share of 42.53 percent (3rd Advance Estimate).
Why has the government restricted wheat
stocks?
·
The revised stock
limits are meant to stop organizations involved in wheat stocking from
hoarding. The government intends to discourage artificial scarcity and ensure a
fair distribution of wheat among various stakeholders by imposing stricter
limits.
·
The imbalance
between supply and demand that results from excessive hoarding can have a
negative impact on consumers and cause price fluctuations.
·
The availability
of sufficient quantities on the market to meet the nation's food requirements
is ensured by regulating wheat stocks. By preventing food shortages and ensuring
that consumers have access to this essential food, it contributes to food
security.
What is the current situation regarding
the nationwide distribution of wheat?
·
After China,
India is the world's second-largest wheat producer. However, it only contributes
less than 1% of global wheat trade. It keeps a lot of it to give poor people
free food.
·
Uttar Pradesh,
Punjab, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, and Gujarat are India's
major wheat-growing states.
·
Major
Destinations for Export (2022-23): Bangladesh, Indonesia, Korea Rep.
MENTAL HEALTH INITIATIVES

·
The country's
initiatives to address mental health issues have been made clear by the
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
What initiatives in mental health are
highlighted?
Public Emotional well-being System
(NMHP):
·
Initiated in 1982
and reorganized in 2003, the NMHP aims to upgrade psychiatric wings in medical
facilities and modernize mental health facilities.
·
Additionally, the
District Mental Health Programme (DMHP) has focused on primary healthcare-level
community mental health services in 716 districts since 1996.
·
At community
health and primary health centers, DMHP provides outpatient services,
counseling, psychosocial interventions, and support for severe mental
disorders.
·
They all come
together to form a comprehensive plan for mental health care in India.
Program for Telemental Health in the
Nation:
·
In order to
further expand nationwide access to high-quality mental health counseling and
care, NTMHP was launched in October 2022.
·
The National Apex
Centre for Tele MANAS's coordination of activities across India is the National
Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS) in Bengaluru.
·
25 States/UTs
have laid out 36 Tele Psychological well-being and Business as usual Expansion
Frameworks (MANAS) Cells for broadening psychological well-being
administrations.
·
Taking care of
63,806 calls made to the helpline number in total.
Collaboration Between iGOT-Diksha and
NIMHANS:
·
Through the
(iGOT)-Diksha platform, NIMHANS provides psychosocial support and training.
·
NIMHANS offers
health care workers online training on the (iGOT)-Diksha platform.
Ayushman Bharat - HWC Plan:
·
The Ayushman
Bharat - Wellbeing and Health Focuses (Stomach muscle HWCs) are essential for
the Ayushman Bharat Program.
·
Preventive,
curative, rehabilitative, and palliative care (a specialized medical approach
that aims to improve the quality of life for people with serious illnesses) are
among the services that the program aims to provide.
·
Functional rules
on Mental, Neurological, and substance use issues (MNS) at Wellbeing and Health
Focuses (HWC) have been delivered under the ambit of Ayushman Bharat.
Tending
to Pandemic-Instigated Emotional wellness Difficulties:
·
A 24-hour
helpline that provides psychosocial support to various population groups has
been established by the government.
FOOD SECURITY

·
The Food and
Agribusiness organisation (FAO) of the Assembled Countries has sent off the
Asia-Pacific Provincial Outline of Food Security and Nourishment 2023:
According to Statistics and Trends, 74.1 percent of Indians would not be able
to afford a healthy diet in 2021.
What are the Report's Most Important
Highlights?
Global:
·
In the
Asia-Pacific region, the rate of undernourishment fell to 8.4% in 2022 from
8.8% the previous year. This represents approximately 12 million fewer people
than in 2021, but 55 million more than in 2019, prior to the Covid-19 pandemic.
·
With 370.7
million undernourished individuals, the Asia and the Pacific area addresses
half of the world's undernourished individuals.
·
Nearly 314
million people in Southern Asia suffer from malnutrition. This addresses 85 %
of undernourished individuals in the Asia and the Pacific area.
·
There are all the
more seriously food uncertain people in Southern Asia than some other
subregions.
·
Except for
Eastern Asia, women tend to be more food insecure than men across the
subregions.
Indian:
·
Unaffordability
of a Healthy Diet: In 2020, 76.2 percent of Indians were unable to afford a
healthy diet, up from 74.1 percent in 2021.
·
Comparative
Analysis with Other Countries: Pakistan had 82.2% and Bangladesh had 66.1% of
their populaces confronting hardships in getting to good food.
·
Regional Food
Security and Nutrition: India's population is malnourished by 16.6%.
Since
2015, the global prevalence of moderate, severe, and severe food insecurity has
decreased in India.
·
Youngsters'
Wellbeing: 31.7 percent of children under the age of five were stunted, and
18.7 percent of those children were wasting, or having a weight that was too
low for their height.
·
Under 5% is the
WHO's global nutrition target for childhood wasting.
·
Poor nutrition
and maternal health, inadequate feeding practices for infants and young
children, and persistent infections in conjunction with a variety of other
factors lead to stunted growth and development.
·
Ladies'
Wellbeing: 53% of the country's ladies matured between 15 to 49 had pallor,
which was the biggest commonness rate in India in 2019.
·
Women's health
and well-being are negatively impacted by anemia, as is the likelihood of
adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes.
·
Weight and
Nourishment Pointers: The FAO estimates that as of the year 2000, 1.6% of
adults in the nation were obese. By 2016, the percentage had increased to 3.9%.
·
Select
Breastfeeding: India has increased the prevalence of exclusive breastfeeding
among infants between the ages of 0 and 5 months to 63.7%, which is higher than
the global prevalence of 47.7%.
·
India has the
most noteworthy pervasiveness of low birthweight in the district (27.4%),
trailed by Bangladesh and Nepal.
What is the Food and Farming
Association?
About:
·
The United
Nations' FAO is a specialized agency that leads international efforts to end
hunger.
·
World Food Day is
commended consistently all over the planet on sixteenth October. The day is
commended to stamp the commemoration of the establishing of the FAO in 1945.
·
It is based in
Rome (Italy) and is one of the UN agencies that provide food aid. The World
Food Programme and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD)
are its sister organizations.
GLOBAL REPORT ON ROAD SAFETY
·
The Global Status
Report on Road Safety 2023, published by the World Health Organization (WHO),
provides important information about road traffic fatalities and safety
worldwide.
What are the Report's Most Important
Highlights?
Fatalities in Car Traffic:
·
Between 2010 and
2021, the number of people who died as a result of traffic accidents worldwide
decreased by 5%, to 1.19 million annually.
·
During this time,
108 UN member nations reported a decrease in road traffic fatalities.
·
The number of
fatalities in India increased by 15% from 1.34 lakh in 2010 to 1.54 lakh in
2021.
States with Significant Decreases:
·
Over 50% of road
traffic fatalities were reduced in ten nations: Venezuela, Belarus, Brunei
Darussalam, Denmark, Japan, Lithuania, Norway, the Russian Federation, Trinidad
and Tobago, and the United Arab Emirates
·
Thirty-five
additional nations made significant progress, reducing deaths by 30 to 50
percent.
Distribution of Deaths by Region:
·
WHO's South-East
Asia Region was responsible for 28%, the Western Pacific Region for 25%, the
African Region for 19%, the Americas Region for 12%, the Eastern Mediterranean
Region for 11%, and Europe for 5% of all road traffic deaths worldwide.
·
Despite having
only 1% of the world's automobiles, low- and middle-income nations bear a
disproportionate burden, with 90% of deaths occurring in these nations.
Road
Users Who Are at Risk:
·
53% of all street
traffic fatalities are weak street clients, including walkers (23%), riders of
fueled two-and three-wheelers (21%), cyclists (6%), and clients of miniature
portability gadgets (3%).
·
Between 2010 and
2021, cyclist deaths increased by nearly 20% to 71,000, while pedestrian deaths
increased by 3% to 274,000.
·
However, car and
other four-wheeled light vehicle occupant deaths decreased slightly, accounting
for 30% of global fatalities.
Policies and safety standards are moving
forward:
·
While 140
countries, or two-thirds of UN Member States, have laws that meet WHO best
practice for at least one of these risk factors, only six countries have laws
that meet WHO best practice for all risk factors (speeding, drinking and
driving, and using motorcycle helmets, seatbelts, and child restraints).
·
Only a small
number of nations have laws that mandate safety inspections for motorists and
cover key vehicle safety features.
Call for Activity:
·
By 2030, the
world's motor vehicle fleet is expected to double, necessitating strict safety
regulations and infrastructure enhancements.
·
The goal of
halving the number of people killed in traffic accidents by 2030 set by the
United Nations Decade of Action 2021–2030 is outlined in the report.
What are the Drives Connected with
Street Wellbeing?
Global:
Declaration of Brasilia on Road Safety
(2015):
·
At the second
Global High-Level Conference on Road Safety in Brazil, the declaration was
signed. The Declaration was signed by India.
·
The nations
intend to accomplish Economical Improvement Objective 3.6 i.e., to divide the
quantity of worldwide passings and wounds from street auto collisions by 2030.
Action Plan for Road Safety from 2021 to
2030:
·
The ambitious
goal of preventing at least 50% of deaths and injuries caused by traffic
accidents by 2030 was adopted by the UN General Assembly in the resolution
"Improving global road safety."
·
By emphasizing
the significance of a comprehensive approach to road safety, the Global Plan
adheres to the Stockholm Declaration.
Engine Vehicles Change Act, 2019:
·
The Act increases
the penalties for traffic violations, vehicle defects, driving while underage,
and other offenses.
·
It establishes a
Motor Vehicle Accident Fund that mandates insurance coverage for certain kinds
of accidents for all road users in India.
·
It also calls for
the Central Government to establish a National Road Safety Board.
The
2007 Carriage by Road Act:
·
The Act regulates
common carriers by limiting their liability and requiring them to declare the
value of the goods they deliver to determine their liability for loss or damage
caused by themselves, their servants, or agents' negligence or criminal acts,
as well as for related or incidental matters.
The Land and Traffic Control of National
Highways Act of 2000:
·
Control of land
within the National Highways, right of way, and traffic moving along the
National Highways, as well as the removal of unauthorized occupation thereon,
are all governed by the Act.
Indian National Highways Authority Act
of 1998:
·
The Act
establishes a body to be responsible for the creation, upkeep, and management
of NHs as well as any related or unrelated issues.
