BRI
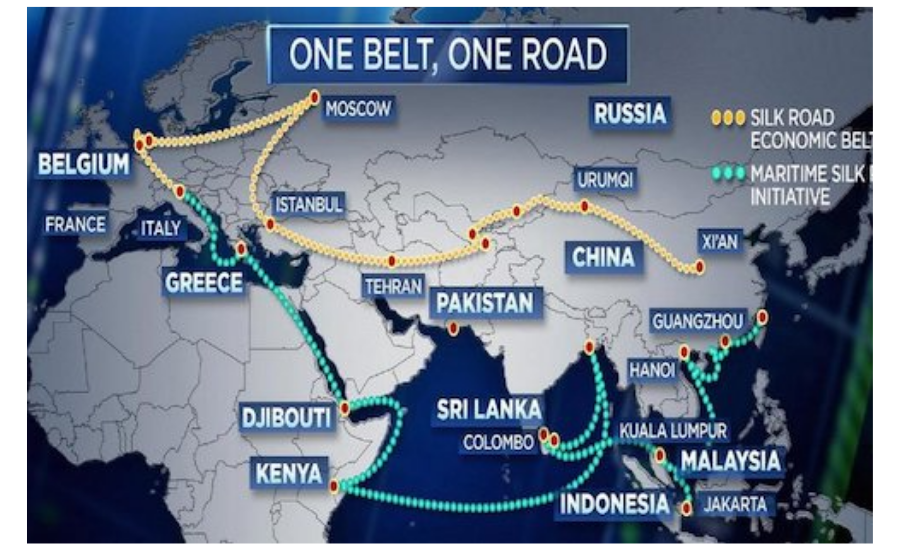
·
Italy
has withdrawn from China's Belt and Street Drive, over four years subsequent to
turning into the main G7 country to join.
·
Italy's
expected withdrawal from China's BRI originates from a mix of financial,
international, and key factors that have driven the country to rethink its
support.
What are
Italy's reasons for leaving the BRI?
Financial
Unevenness:
·
Italy
had joined the BRI in 2019 all at once it was frantic for speculation and
framework building, having endure three downturns in 10 years.
·
Notwithstanding,
the expected financial advantages haven't emerged as in these four years after
the fact, the arrangement hasn't done much for Italy.
·
Chinese
FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) in Italy decreased from USD 650 million in 2019
to just USD 33 million in 2021, according to data from the Council on Foreign
Relations.
·
Regarding
exchange, since joining BRI, Italy's commodities to China expanded from 14.5
billion euros to a simple 18.5 billion euros, while Chinese products to Italy
extended from 33.5 billion euros to 50.9 billion euros.
International
Realignment:
·
The
rethinking of Italy's relationship with China is part of a larger trend among
European nations to reevaluate their ties to China.
·
Worries
over China's rising impact, international arrangements, and vital
ramifications, especially in the midst of worldwide occasions like the
Russia-Ukraine struggle, have provoked Italy to reconsider its position toward
the BRI.
·
The
Comprehensive Agreement on Investment (CAI) between China and the EU broke down
in April. Last year, Estonia and Latvia quit the 17+1, China's political push
in Focal and Eastern European nations. Lithuania had left in 2021.
Alignment
with Allies in the West:
·
Italy's
tendency to adjust itself all the more intimately with its Western partners,
particularly in the G7, could impact its choice in regards to the BRI.
·
With
the G7 administration forthcoming, Italy could consider passing on the BRI to
be a token of fortitude with Western partners.
Negative
Press and Obligation Concerns:
·
The
BRI has confronted analysis around the world for potential obligation traps and
absence of straightforwardness in monetary dealings.
·
Reports
of different nations confronting significant obligation loads because of their
support in the BRI may be adding to Italy's Withdrawal.
How Have
India-Italy Relations Been?
Cultural
and Historical Connections:
·
India
and Italy share old ties that date back millennia, with verifiable associations
through shipping lanes and social trades.
·
People
like Mahatma Gandhi and Rabindranath Tagore have had significant interactions
with Italy, which has contributed to the history of their relations.
Difficulties
in Respective Relations:
·
Italian
Marines Case: In 2012, the case including two Italian marines blamed for
killing Indian anglers off the Kerala coast stressed relations. The issue
heightened strategically and legitimately, affecting conciliatory ties between
the nations. The case was in the long run settled after remuneration was paid
by Italy to India, shutting in 2021.
·
Agusta
Westland Claims: Debasement claims with respect to the AgustaWestland bargain
additionally stressed relations. Italy and India filed lawsuits as a result of
investigations into unethical dealings and corruption in a significant defense
contract.
·
Regardless
of the dropping of the agreement and judicial procedures, the Italian courts
excused all charges because of lacking proof.
Endeavors
towards Fix:
·
Discretionary
Commitment: Endeavors to retouch ties started around 2018. Official visits,
social trades, and significant level commitment between authorities from the
two nations planned to reconstruct relations.
·
Key
Associations: Indian State head's visit to Italy for the G20 culmination in
2021 and resulting commitment with Italian administration checked huge
achievements. Two-sided arrangements and key associations were laid out,
zeroing in on different areas like protection, exchange, and innovation.
·
Monetary
Participation: Respective exchange has seen critical development, with Italy
arising as a key exchanging accomplice for India inside the EU. The focus on
economic cooperation, which has led to collaborations in technology, defense,
and other areas, has made ties stronger.
·
Reconsidering
Commitment with China: India and Italy have both rethought how they work with
China, especially with regard to projects like the Belt and Road Initiative
(BRI). India's opposition to the BRI is based on territorial concerns, and
Italy's rethinking of the BRI is driven by economic imbalances and unmet
expectations.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE

·
The
European Union (EU) has made way for the world's most memorable thorough
regulation pointed toward managing the utilization of Man-made consciousness
(artificial intelligence).
·
The
EU's proposed system will go through a parliamentary vote in mid-2024, possibly
becoming enforceable by 2025.
What are the Critical Parts of the EU System for artificial
intelligence Guideline?
Shields in Regulation:
·
Strengthening of Buyers: Capacity for people to send off grievances against saw
man-made intelligence infringement.
·
Limitations on Policing: Clear limits on computer based intelligence utilization by
policing.
·
Severe Limits on computer based intelligence: Solid limitations on facial
acknowledgment innovation and man-made intelligence control of human way of
behaving.
·
Punishments for Infringement: Arrangement for intense punishments for organizations
tracked down defying the norms.
·
Restricted Biometric Reconnaissance: State run administrations allowed to involve ongoing
biometric observation in open regions just in instances of serious dangers like
fear based oppressor assaults.
Order of computer based intelligence Applications:
·
Four Gamble Classes: Man-made intelligence applications arranged into four gamble
classifications in view of their degree of chance and obtrusiveness.
·
Restricted Applications: Mass-scale facial acknowledgment and conduct control
artificial intelligence applications are to a great extent prohibited, with
exclusions for policing.
·
High-Hazard Applications: Permitted with affirmation and arrangement for backend
strategy straightforwardness, for example, man-made intelligence apparatuses
for self-driving vehicles.
·
Medium-Hazard Applications: Deployable without limitations, as generative computer
based intelligence chatbots, with express revelation to clients about simulated
intelligence cooperation, straightforwardness commitments, and itemized tech
documentation.
Other EU's Administrative Accomplishments:
·
General data protection regulation (GDPR) Execution: Implemented since May 2018, zeroing
in on security and unequivocal assent for information handling.
Sub-Legislations: DSA and DMA:
·
Digital service act (DSA): Center around controlling disdain discourse, fake products,
and so forth.
·
Digital Markets Act (DMA): Recognizing "prevailing watchman" stages and
tending to non-cutthroat practices and strength misuse.
What is India's System In regards to computer based
intelligence Guideline?
Stance:
·
India
is yet to have a thorough structure for managing computer based intelligence.
Be that as it may, India has moved from a position of not considering man-made
intelligence guideline to effectively forming guidelines in light of a gamble
based, client hurt approach.
GRAM MANCHITRA AND M-ACTION

·
The
ministry of Panchayati Raj presented "Gram Manchitra," a Geographic
Data Framework (GIS) application.
·
Furthermore,
the Service sent off "mActionSoft," a portable based answer for
geo-labeling project resources.
What is Gram Manchitra and mActionSoft?
Gram Manchitra:
·
About:
The essential objective of Gram Manchitra is to energize spatial arranging
drives by Gram Panchayats, utilizing the abilities of geo-spatial innovation.
·
The
application upholds the Gram Panchayat development Plan (GPDP) by helping
navigation.
Features:
·
Brought together GeoSpatial Stage: Gram Manchitra gives a solitary and brought together stage,
working with the representation of formative ventures and exercises at the Gram
Panchayat level.
Area Wise Preparation: It empowers Gram Panchayats to design and execute formative
works across various areas, encouraging an all encompassing way to deal with
country improvement.
Advancement Plan Instruments: Apparatuses incorporate undertaking site recognizable
proof, resource following, cost assessment, and venture influence appraisal.
M Action Soft:
·
About:
mActionSoft is a versatile based arrangement, assumes a significant part in
catching geo-labeled photographs with GPS organizes for works with resource
yields.
Resources go through geo-labeling at three phases: prior to the beginning
of work, during the work, and upon finishing.
·
This
lays out a complete vault of data on different works connected with regular
asset the executives, water collecting, sterilization, farming, and that's just
the beginning.
Features:
·
Geo-Tagging:
Panchayats geotag resources made under finance commission assets with photos,
guaranteeing straightforwardness and responsibility.
·
The
resources geo-labeled utilizing mActionSoft consistently coordinate with Gram
Manchitra, enhancing the perception of formative works in Gram Panchayats.
·
Geographic
Data Framework: An innovation catches, makes due, investigations, and presents
topographical or spatial information.
·
It
permits clients to envision, decipher, and comprehend information by connecting
it to areas on the World's surface.
·
GIS
joins different layers of data like guides, satellite symbolism, and
information tables to make intuitive guides and models.
·
It
is utilized in assorted fields like metropolitan preparation, ecological
examination, regular asset the executives, crisis reaction, and that's only the
tip of the iceberg, helping with navigation and critical thinking connected
with spatial data.
·
Geotagging:
It is the method involved with adding geological distinguishing proof to
different media, for example, photographs, recordings, sites, or different
archives.
·
It
includes appending metadata, as rule GPS directions to these records, giving
explicit area data about where the media was made or caught.
·
This
empowers clients to pinpoint the specific geographic area related with the
substance, working with association, search, and planning of information in
view of its area.
SHORT RANGE – AGNI 1

·
Send
off of Short-Reach Long range missile 'Agni-1' was done effectively from Dr. APJ
Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha. The send off, did under the aegis of the Essential
Powers Order, effectively approved all functional and specialized boundaries.
What is Long range missile 'Agni-1'?
About:
·
The
Agni-1 is a Short-Reach Long range missile (SRBM) created by India as a feature
of its Agni series of rockets. It is the principal rocket in the Agni series
and is intended to be an essential weapon equipped for conveying an atomic
payload.
·
The
Agni-1 is principally planned for use as an obstruction against likely foes and
is known for its speedy reaction time.
·
It
is the primary variation of the Agni series rockets under Integrated Guided
Missile Development Program (IGMDP).
Specialized Particulars:
·
The
Agni-1 is a solitary stage, strong energized rocket with a scope of around 700
to around 1200 kilometers and can convey a payload of 1,000 kg, making it a
short-range long range rocket. It has the capacity to convey both regular and
atomic warheads.
·
The
strong fuel impetus framework upgrades its functional adaptability and
decreases sendoff planning time.
Advancement and Testing:
·
The
Agni-1 was created by the Defence research and development organization (DRDO)
in India. The rocket has gone through a few fruitful test dispatches to approve
its presentation and unwavering quality.
·
Agni-1
was first tried at the Break Test Reach in Chandipur in 1989. The Indian armed
force acknowledged Agni-1 in assistance in 2007.
What are the Other Agni Class of Rockets?
·
The
Agni series is a group of long range rockets created by India, with every
variation intended for explicit ranges and purposes. Other than Agni-1, other
outstanding rockets in the series include:
Scope of other Agni Rockets:
·
Agni
II: Range in excess of 2000 km.
·
Agni
III: Scope of in excess of 2,500 Km
·
Agni
IV: Range is in excess of 3,500 km and can fire from a street portable
launcher.
·
Agni-V:
The longest of the Agni series, a Between Mainland Long range Rocket (ICBM)
with a scope of north of 5,000 km.
·
Agni Prime: A
two-stage canisterised rocket (a work in progress) has been effectively flight
tried in June 2023.
·
The
rocket is equipped for conveying various warheads at discrete areas a ways off
of 1,000 - 2,000 km.
ICBMs:
·
It
is a sort of lengthy reach long range rocket with the capacity to travel huge
distances, regularly intercontinental reaches.
·
They
assume an essential part in a country's atomic set of three, which incorporates
land-based rockets, submarine launch ballistic missile (SLBMs), and key planes.
·
ICBMs
are portrayed by their incredibly lengthy reaches, regularly surpassing 5,500
kilometers (around 3,400 miles) and frequently arriving at distances of north
of 10,000 kilometers (in excess of 6,200 miles).
·
ICBMs
follow a ballistic direction, meaning they are sent off into space before
returning the World's environment to strike their objectives.