H3N2 Virus
India has recorded deaths of two people, one each in Karnataka and Haryana, due to the Influenza A subtype H3N2 virus, the government said on Friday. It added that around 90 cases of this virus have been reported across the country.
What is the H3N2 virus?
- Influenza viruses, which cause the infectious disease known as flu, are of four different types: A, B, C and D. Influenza A is further classified into different subtypes and one of them is the H3N2.
- According to the United States’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), H3N2 caused the 1968 flu pandemic that led to the death of around one million people globally and about 100,000 in the US.
- A 2020 study, published in the journal Nature Communications, found that the strains of the virus have dramatically evolved in the past five decades as people born in the late 1960s and 1970s got infected by it as children.
What are the symptoms of H3N2?
- Its symptoms are similar to that of any other flu.
- They include cough, fever, body ache and headache, sore throat, a runny or stuffy nose and extreme fatigue.
- Nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea have been seen in very few cases.
- According to the Indian Medical Association (IMA), an infection caused by H3N2 generally lasts for five to seven days and the fever starts going away after three days.
- However, the coughing can persist for up to three weeks.
- As per the IMA, this virus usually preys on individuals below the age of 15 years or above 50 years of age. Children and those with co-morbidities like asthma, diabetes, heart disease, weakened immune systems and neurological or neurodevelopmental conditions are at a higher risk.


Multi-Angle Imager for Aerosols mission
Recently, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) announced on Wednesday that it is partnering with the Italian Space Agency ASI (Agenzia Spaziale Italiana) to build and launch the MAIA mission.
Multi-Angle Imager for Aerosols
The Multi-Angle Imager for Aerosols (MAIA) is a joint mission between NASA and the Italian Space Agency ASI.
The mission’s primary objective is to investigate the health impacts of air pollution in major cities across the world.
Collaboration for Societal Health:
- Epidemiologists and public health researchers will work directly on the development of the satellite mission to benefit societal health.
- The PLATiNO-2 satellite, provided by ASI, will be equipped with a science instrument built at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) to achieve the mission objectives.
Observatory and Data Collection:
- The MAIA mission will collect and analyse data from the observatory, sensors on the ground, and atmospheric models.
- The JPL hosts a pointable spectropolarimetric camera that captures images from multiple angles in the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, and shortwave infrared portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Target Areas:
- During the three-year mission, MAIA will focus on 11 primary target areas, including major urban centres across the world such as Los Angeles, Atlanta, Boston, Rome, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, Barcelona, Spain, Beijing, Johannesburg, New Delhi, Taipei, Taiwan, and Tel Aviv.
- The selection of these target areas reflects their high population density and varying levels of air pollution.
Launch and Timeline:
- The MAIA observatory is set to launch before the end of 2024.
- The mission will continue for three years, during which time data will be collected, analysed, and studied to gain insights into the health impacts of air pollution in major cities worldwide.

Digital India Bill, 2023
The Central government has formally outlined the Digital India Bill, 2023.
- The Central government formally outlined the Digital India Bill, 2023. The Act will replace the decades-old Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Minister of State for Electronics and Information Technology, Shri Rajeev Chandrasekhar, announced that the government is reconsidering a key aspect of cyberspace — ‘safe harbour’.
- Safe harbour is the principle that so-called ‘intermediaries’ on the internet are not responsible for what third parties post on their website.
- This is the principle that allows social media platforms to avoid liability for posts made by users.
- The Minister said that intermediaries for which safe harbour was applied as a concept have now morphed into multiple types of participants and platforms on the internet.
- They are now functionally very different from each other, and will require different types of guardrails and regulatory requirements.
- The Minister also said that the constitutional protections for freedom of expression, under Article 19, will be given priority over in comparison to social media platforms’ own moderation policies.
Background -
- The Central government in December 2022 had released the draft Digital India Bill for public consultation by the end of this month.
- The Digital India Act will subsume the Information Technology Act 2020, which according to experts and government officials need a revamp owing to changing internet scenarios.
- The proposed bill, alongside the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Bill, 2022 whose draft was released recently, will contribute to the evolving framework which is light on regulation, safeguards consumer rights and catalyses innovation.
Key aspects of Digital India Bill -
- The government is considering a departure from the long-held understanding of ‘intermediaries’ on the Internet – sites that typically act as a platform for users to access services on the Internet.
Present Scenario –
Under the Information Technology Act, 2000, there is no classification of intermediaries.
Proposal –
- The new law will prescribe different kinds of intermediaries because their regulation has to be different.
- Intermediaries will be bucketed as social media platforms, e-commerce platforms, AI platforms, fact-checking platforms etc.
New Regulator for Internet –
- The new Bill is also expected to prescribe a new regulator for the online space along the lines of the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) or the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- The new law is also expected to introduce penal consequences for violations, and prescribe governing provisions for emerging technologies like the metaverse and blockchain.
- Once finalised, the Bill will impact Big Tech companies like Google, Amazon, Meta, Amazon and Apple, among others.
Why is the Digital India Act important?
- Since IT Act, 2000 the Digital India Act will be the most significant piece of IT legislation as it will potentially govern the entire country’s digital laws for the next decade or two.
- With this new law, the country hopes to future-proof its digital laws and enable businesses to compete on a global scale.
- The Digital India Act will be designed to stimulate the digital economy for Indian businesses and transform the nation into a worldwide digital powerhouse.
- The Government believes India can achieve a trillion-dollar digital economy by 2026, centred around the Digital India Act.
About Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2022 -
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology formulated a draft Bill, titled ‘The Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2022’.
- The purpose of the draft Bill is to provide for the processing of digital personal data in a manner that recognises both the right of individuals to protect their personal data and the need to process personal data for lawful purposes.
- The Bill frames out the rights and duties of the citizen (Digital Nagrik) on one hand and the obligations to use collected data lawfully of the Data Fiduciary on the other hand.

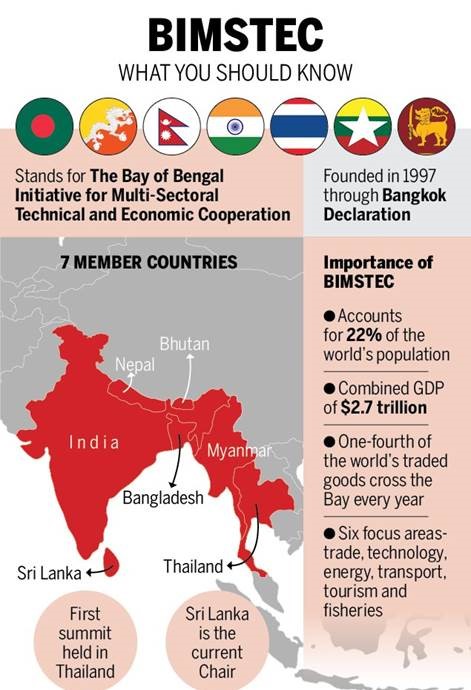
19th The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) Ministerial Meeting virtually from Bangkok
Recently, the Minister of State for External Affairs participated in the 19th The Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) Ministerial Meeting virtually from Bangkok.
About BIMSTEC Ministerial Meeting -
- During the meeting, the Ministers approved several documents including rules of Procedure for Core BIMSTEC Mechanisms, Sectoral BIMSTEC Mechanisms and BIMSTEC’s External Relations for submission to the 6th BIMSTEC Summit.
- The meeting also approved the draft Host Country Agreement between India and the BIMSTEC Secretariat for establishing BIMSTEC Centre for Weather and Climate in India.
- The Meeting also approved the Terms of Reference for an Eminent Person’s Group on the Future Directions of BIMSTEC.
- The Terms of Reference were finalised under the special scheme for institution building.
- Besides BIMSTEC Bangkok Vision 2030 was also approved and will be launched at the 6th BIMSTEC Summit.
- The Meeting also gave its nod to the Administrative and Disciplinary Rules of the Secretariat and amended Financial Rules and Regulations of the BIMSTEC Secretariat.
About BIMSTEC -
- It is a regional organisation that was established on 06 June 1997 with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration.
- Member countries — Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan and Nepal
- The Chairmanship of BIMSTEC rotates according to the alphabetical order of the English names of the Member States.
- During the Third BIMSTEC Summit, the Secretariat was established in Dhaka, Bangladesh.

Kinzhal Missile
Russia recently fired hypersonic Kinzhal missiles as part of a massive wave of strikes on Ukraine.
About the ‘Kinzhal Missile’ -
- The Kh-47M2, nicknamed "Kinzhal" (Dagger), is a nuclear-capable, Russian air-launched ballistic missile.
- It was one of six “next generation” weapons unveiled by Russian President Putin during a speech in March 2018.
Features —
- The Kinzhal can reach speeds of up to Mach 10 (12,350 km/hr).
- It can carry both conventional and nuclear warheads with a payload of up to 480 kg and a thermonuclear option with a 10-50 kt warhead.
- It has a reported range of 1,500-2,000 km.
- The Kinzhal has a length of 8 m, a body diameter of 1 m, and a launch weight of approximately 4,300 kg.
- It is designed to be launched from MiG-31 fighter jets at altitudes of about 18 km (59,000 ft).
- This missile maneuvers during all stages of its flight to overcome hostile air defense systems.
What are Hypersonic Missiles?
- A hypersonic missile is a weapon system which flies at least at the speed of Mach 5 i.e. five times the speed of sound and is manoeuvrable. These missiles are extremely fast and far harder for surface-to-air missile defence systems to target.